This article will answer the question “does a wasp die when it stings you”. Let’s learn about this important topic and many other related topics in detail in the coming few lines.
Wasp stings are expected, mainly during the warmer months when individuals are out for extended periods. They can be extremely painful, but most people heal quickly and without consequences. Wasps, like bees and hornets, have a stinger for self-defense. A wasp’s stinger has venom (a poisonous substance) transferred to humans during a sting.
However, the wasp venom can cause considerable pain and discomfort without an installed stinger. It’s also likely that you will experience a severe response if you’re allergic to the toxin. In either possibility, quick treatment is crucial for clearing symptoms and reducing health risks.
Page Contents
Symptoms of a wasp sting
- Symptoms of a wasp sting: Most people without sting allergies will demonstrate only minor symptoms during and after a wasp sting. The initial reaction may involve a sharp pain and burning feeling in the sting area. In addition, redness, swelling, and Itching will likely happen.
- Normal local reactions: You’re likely to experience a raised bump around the sting area. A tiny white spot may be visual in the seat of the node where the stinger spiked your skin—usually, the pain and swelling decrease within several hours of being stung.
- Large local reactions: “Large local reactions” is an expression for more noticeable symptoms associated with a wasp or bee sting. Individuals who have marked local responses may be allergic to wasp stings. Still, they don’t manifest life-threatening events such as an anaphylactic response.
Significant regional responses to wasp stings involve redness and swelling that can be visible for two or three days after the sting. Nausea and vomiting can also occur. Most of the time, significant local responses subside within a week or so.
Do wasps die when they sting you?
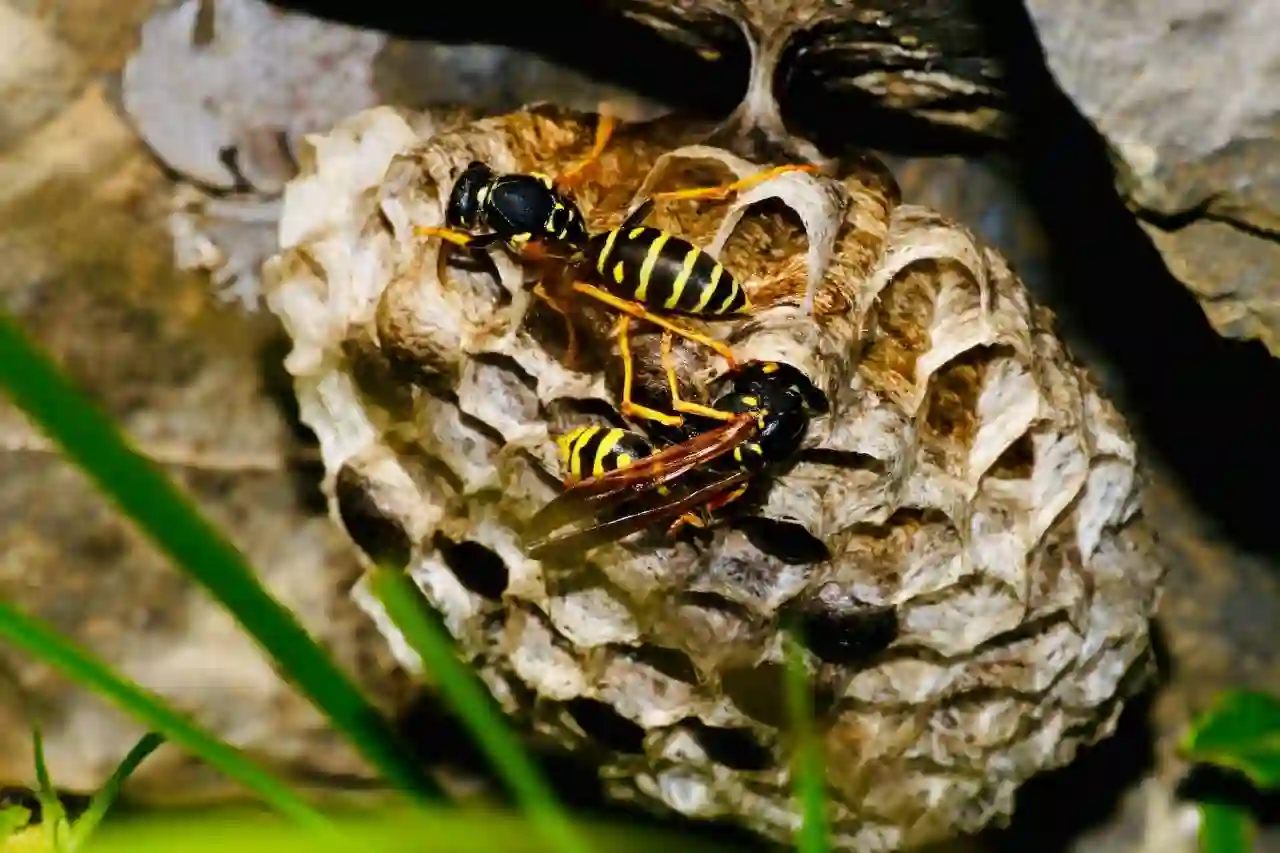
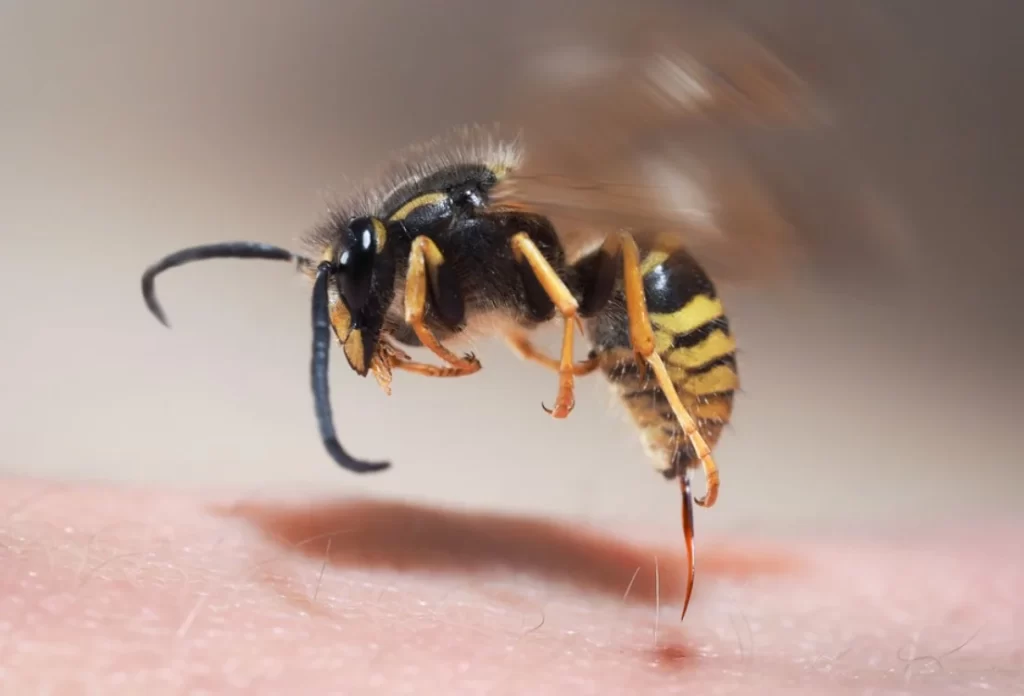
Unlike bees, wasps don’t die when they sting humans. They will prick numerous folks multiple times throughout their lifetime. A wasp’s stinger isn’t a bee’s stinger. It’s designed to be used more than once.
A bee’s stinger is barbed at the top, which is why a bee can sting, then die. Once the bee dashes, the stinger stays within the prey’s flesh and disembowels the bee. A wasp’s stinger is wiggled and doesn’t stick in a person’s flesh. It retracts into the body, ready to extend over and once again.
Wasps can attack in massive numbers. Once a threat is detected, wasps unharness a secretion that summons the remainder of the soldier wasps. They’ll pursue a possible threat over long distances and swarm the danger, stinging repeatedly.
Will a wasp sting you for no reason?
A wasp will rarely sting without a good reason. As a rule, they only sting and bite when they feel threatened. This occurs when a person has accidentally stepped on a wasp nest.
Wasps will go to great lengths to protect their colonies. In the wild, they use their stingers to defend their nesting areas and territories from intruders.
The same defensive rationale drives their employment of this method on humans. . On the other hand, solitary wasps rarely sting unless they are provoked.
Can a wasp sting if you keep still?
If a wasp lands on you, do not flap at it or try and brush it off – it can sting you. Keep still and let it fly off on its own.
However, it is more challenging if a wasp lands on your clothes as any slight movement will press clothes against it and gets it irritated.
What do you do if a wasp lands on you?
- Stay Calm: The easiest and, therefore, the hardest at the same time is staying calm after seeing a wasp, knowing that there’s an opportunity to get stung. Our past experiences or information concerning wasps, calls on our nerves.
- Stay passive, and avoid aggression: The most common mistake that results in an unwanted sting is attempting to kill a wasp. This sometimes works, but most of the time does not. Aggression makes it worse, as you are perceived as a credible threat to the wasp. You can imagine the outcome of a failure in killing a wasp.
- Defensive instinct – sting: Gently and slowly brush it away with a chunk of paper. Brushing the wasp off is better than smashing it because it’ll sting you if you use the latter technique. Of course, never grasp a wasp if it lands on you. This is also a risky strategy.
How do you know if a wasp is angry?
Scientists have discovered a way to tell whether a wasp is angry (before it stings you, of course). Anger can be seen on the wasp’s face/head.
Wasps present hostility through the markings on their heads. The more black spots they present, the angrier they are.
Can wasps sting through clothes?
The short answer: Yes!
In most cases, wasps can sting through clothes. Wasps have a sharp, pointed stinger that they use to inject venom into their victims. And the stinger is able to penetrate most types of clothing.
However, the wasp’s stinger cannot penetrate all materials. Heavy fabrics or thick layers of clothing may provide some protection against wasp stings.
It is also worth noting that wasps may be more likely to sting if they become trapped between a person’s skin and tight-fitting clothing.
For this reason, it is generally best to avoid wearing clothing that is too tight or constricting when around wasps.
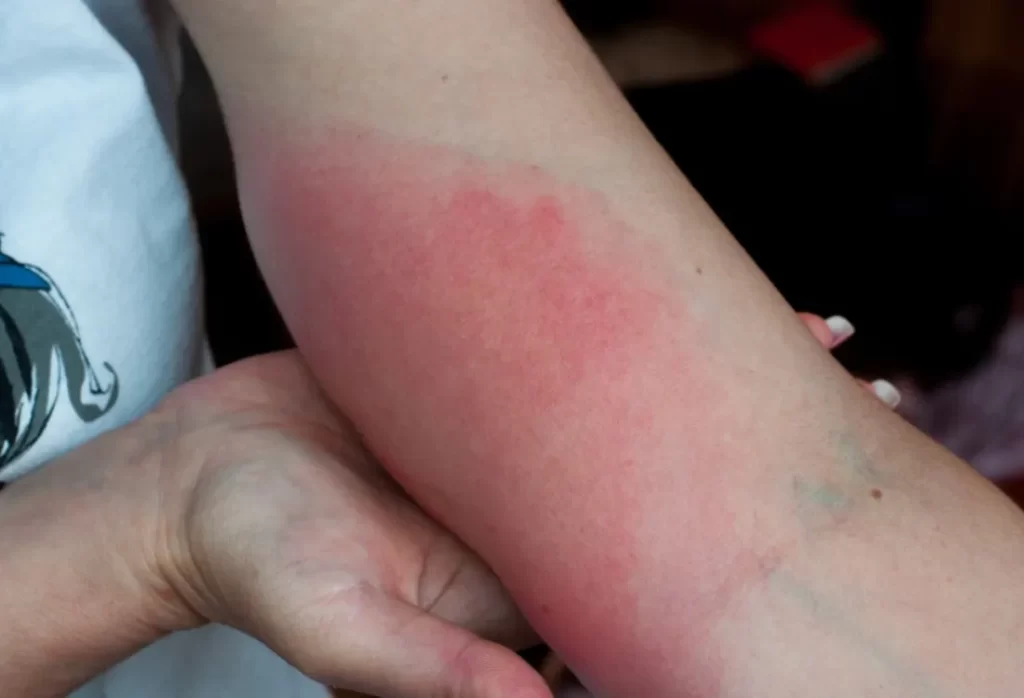
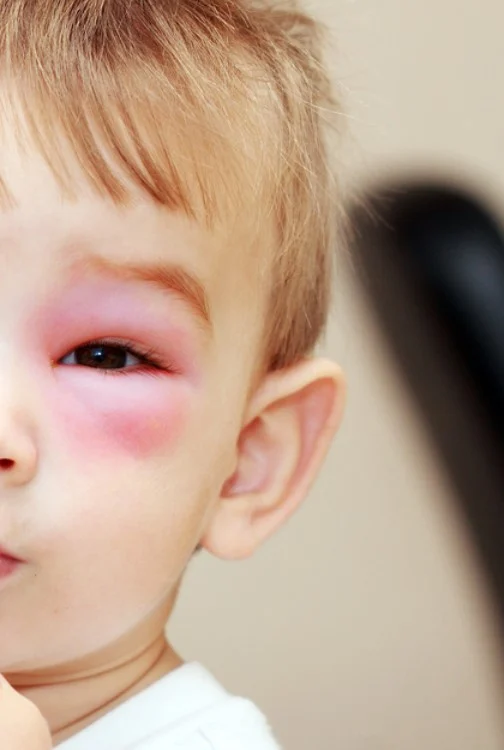
What does a wasp sting look like?
When was the first time you witnessed a wasp sting? Maybe you’ve even been through one. We hope not. The common reaction to a wasp sting is a raised, red bump. Additionally, it hurts when touched.
Perhaps the bump is no bigger than a standard pencil eraser (around 1/4 inch in diameter). A red, inflamed patch of the size of a quarter may surround it (approximately 1 inch in diameter).
At the epicenter of the sting, you might notice a white or yellow mark.
The stinger made a hole here. Wasp stings typically result in a bump, but there may be additional side effects as well.
The stung site may become itchy, swollen, and hot. Wasp stings can cause mild to severe reactions in humans.
Those symptoms may include, but are not limited to, trouble breathing, nausea, and dizziness. These signs and symptoms should be taken very seriously as they could be life-threatening.
Wasp sting pictures
How painful is a wasp sting?
Pain induced by a wasp sting might vary based on a number of variables. These variables include a person’s susceptibility to the poison and the amount of venom injected.
Wasp stings are generally considered to be somewhat unpleasant, with a pain level of roughly 2 to 3 on a scale from 1 to 10.
Nonetheless, some individuals may feel wasp stings with a pain level of 5 to 7 on the same scale.
Notably, the agony from a wasp sting may be intensified if the victim has been stung several times or if they are allergic to wasp venom.
In extreme circumstances, a wasp sting can trigger anaphylaxis, a potentially fatal allergic reaction requiring immediate medical attention.
But how does it compare with a bee’s sting?
Given that everyone’s threshold for pain is different, it is challenging to say whether a wasp or bee sting is more excruciating.
However, because wasp venom includes more peptides that can induce pain and swelling than bee venom, wasp stings typically hurt more than bee stings.
Wasp venom can also trigger an allergic reaction in certain people, which can result in a more serious reaction.
However, both kinds of stings can be excruciatingly painful and need to be treated as after to prevent more issues.
Seek medical help right away if you are stung by a wasp or bee and have extreme pain, swelling, trouble breathing, or any other symptoms.
What happens if a wasp loses its stinger?
A wasp without a stinger is unable to sting. The stinger is a modified ovipositor, which is an organ used to deposit eggs and is associated to the wasp’s reproductive system.
A wasp stings by puncturing the skin and injecting venom into the wound, leaving the stinger behind.
The wasp loses its stinger as well as sections of its reproductive organs as a result of this.
As a consequence, a wasp without a stinger is unable to reproduce.
However, since wasps are social insects that live in colonies, the loss of one stinger has minimal effect on the whole colony.
How long can wasps sting after they die?
After killing a wasp, you’ll feel it is safe to touch them. However, is this the truth? Or are deceased wasps still venomous?
Venom from a wasp sting may continue to produce toxins after the wasp has died. This is done so that the poison, which is stored in a venom gland and delivered into the victim through a muscular reaction, can carry out its intended function.
Upon activation of the reflex, the venom is released, and its effects may last long after the wasp has perished.
The effects will not last forever, and eventually the venom will decay and lose its effectiveness.
A dead wasp cannot sting again; thus, any further stinging is likely the product of a reflex response triggered by another event, such as touching the wasp’s corpse.
After being stung by a dead wasp, thoroughly cleaning the site may help remove any leftover venom and reduce the risk of infection.
How many times can a wasp sting?
Including paper wasps and yellow jackets, the majority of wasps may strike several times.
This is because their stingers are smooth and curved, allowing them to withdraw them after stinging without losing them.
In contrast, honey bees have a barbed stinger that gets lodged in the victim’s skin, limiting them to a single sting before death.
Female wasps may sting several times because, unlike honey bees, they employ their stinger for defense and killing prey, rather than reproduction.
It should be noted, however, that not all wasps can sting several times. Queen wasps, which are bigger and more specialized than other colony members, may only be able to strike one or twice before losing their stinger.
How do you get a wasp sting to go away?
The first thing you should do after being stung by a wasp is scrape the stinger off with your fingernail or a credit card.
This will lessen the amount of venom that gets on your skin. Then, to aid in infection prevention, wash the area with soap and water.
You may use a cold compress or an ice pack to the afflicted region for 10 to 15 minutes at a time to assist minimize discomfort and swelling.
To aid with pain relief and swelling reduction, you may also take an over-the-counter pain medicine such ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
Seek emergency medical assistance if you are allergic to wasp stings or if you have been bitten more than once.
A wasp sting allergic response may be life-threatening and need rapid medical attention.
It’s also crucial to remember that over-the-counter medicines, such as vinegar or baking soda, are ineffective for healing wasp stings and should not be used.
Additionally, there is no proof that lemon juice may treat wasp stings. Lemon juice is not advised as a therapy for wasp stings, despite the fact that it may contain a few modest antiseptic characteristics.
The best course of action after being stung by a wasp is to do the actions listed above and, if required, seek medical treatment.
How long do wasp stings last?
The duration of a wasp sting can vary depending on a variety of circumstances, including an individual’s vulnerability to the venom and the volume of venom injected.
In most situations, a wasp sting will induce pain, redness, and swelling at the location of the sting for a few hours. It is usual for a wasp sting to continue to cause agony and suffering 24 hours after the first bite.
Before progressively subsiding, the symptoms may persist for up to two days.
In some cases, a wasp sting may cause severe symptoms, such as allergic responses.
An allergic reaction to a wasp sting can result in symptoms such as hives, difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, or tongue, dizziness, and nausea.
These symptoms may be life-threatening and necessitate immediate medical care.
If you have been stung by a wasp and are experiencing severe symptoms, such as difficulty breathing or swelling of the face, lips, or tongue, you should seek emergency medical care immediately.
If you are unsure whether your symptoms warrant medical attention, you should always visit a healthcare professional.
Does a wasp sting get worse before it gets better?
A wasp sting may get worse before it goes better in some situations.
The venom from a wasp’s sting can produce discomfort, redness, and swelling at the location of an insect bite.
Initially, these symptoms may be modest, but they might worsen when the body’s immune system reacts to the venom.
After a few hours, the symptoms may peak and then progressively lessen over the next two days.
Should I see a doctor after a wasp sting?
Wasp stings do not generally demand medical attention.
Pain, redness, and swelling caused by a wasp sting are often treatable with simple self-care measures at home.
These treatments may involve removing the stinger, washing the affected area with soap and water, and administering an ice pack or cold compress to reduce pain and swelling.
Pain drugs available without a prescription, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can also be used to alleviate discomfort and reduce swelling.
If you are experiencing severe symptoms following a wasp stung, such as difficulty breathing or swelling of the face, lips, or tongue, you should seek immediate medical attention.
These symptoms may signal a life-threatening reaction to the wasp venom, such as an allergic reaction, requiring immediate medical care.
If you have been stung multiple times or if you are susceptible to wasp stings, you should seek medical attention even if your symptoms are not severe.
A healthcare expert can provide the required treatment and guidance to assist you in managing your symptoms and avoiding negative outcomes.
What kills wasps instantly?
There are numerous strategies for eliminating wasps immediately.
Using an insecticide spray specifically designed to kill wasps is a frequent practice.
These sprays are available at the majority of hardware and home improvement stores and often kill wasps on contact.
Using a DIY wasp trap is a second option for killing wasps fast.
Mix equal amounts of water and sugar in a small container, then add a few drops of dish soap. The sweet concoction will attract the wasps, who will then drown in the water as they attempt to reach the sugar.
In addition to these approaches, you can also try using essential oils that repel wasps, such as peppermint or lemon.
Simply combine a few drops of the essential oil with water in a spray bottle and spray the solution about the area from which you wish to repel wasps.
This strategy is less efficient at eliminating existing wasps, but it can help prevent new wasps from entering the area.
Should I get rid of wasps?
Whether you should eliminate wasps depends on your particular preference and the specific circumstances.
Wasps can be beneficial since their diet of flies and caterpillars helps to manage pest populations.
They can sting if they feel threatened or if their nest is disrupted.
If living near wasps makes you uncomfortable or if you are allergic to their stings, it may be advisable to eliminate them.
To avoid being stung, it is essential to utilize safe and effective ways for eradicating wasps and their nests.
You can call a professional exterminator to remove the wasps, or you can do it yourself with a wasp-killing spray or trap.
Alternatively, if the wasps are not creating any issues and you are not allergic to their stings, you may decide to leave them alone.
In this situation, it is crucial not to disturb the wasps or their nest. Additionally, you should take measures to prevent them from entering your home, such as securing any open food containers and covering sugary drinks and meals.
How can I stop wasps from nesting on my property?
There are several steps you may take to keep wasps from reproducing in your house.
One of the most effective approaches is to eliminate food and water sources that may attract wasps.
Covering garbage cans and fastening outside food and beverage containers can help with this.
Wasp traps can also be used to capture and destroy existing wasps on your property.
Furthermore, you may make your home less appealing to wasps by eliminating potential nesting sites such as wood piles and garbage.
If you continue to have wasp problems, you should seek the advice of a pest control professional.
Recap
To repel wasps, you can take the following measures:
- Eliminate food and water sources that might attract wasps. This can be accomplished by covering garbage cans and securing outside food and beverage containers.
- Use wasp traps to capture and eliminate existing wasps from your property.
- Remove any possible wasp nesting places, such as wood piles or rubbish, from your property to make it less appealing to wasps.
- Consider growing wasp-repellent plants and flowers, such as mint and eucalyptus.
- Avoid using perfumes or colognes with pleasant scents, since these might attract wasps.
If you are stung by a wasp, here are some steps you can take to reduce pain and swelling:
- Take out the stinger as soon as you can. With a credit card or fingernail, the stinger can be scraped out of the flesh. Crushing the venom sac with tweezers can release even more poison into the wound, thus this should be avoided at all costs.
- To prevent infection, wash the affected area with soap and water.
- Applying a cold compress or ice pack to the area can help reduce pain and swelling.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen and acetaminophen may be helpful if the pain and swelling don’t go away.
- If you have difficulty breathing or your face or throat starts to swell up severely after being stung, you need to get medical help immediately.
- Where Can I Purchase Bed Bug Bombs? - January 30, 2023
- Where Can I Buy Something to Kill Bed Bugs? - January 30, 2023
- Where Can I Buy Bed Bug Spray? - January 30, 2023